**Introduction of Vacuum Residue (VR)
In the complex world of oil refining, various products are derived from crude oil through a series of processes, each designed to extract different components with distinct properties and uses. Vacuum Residue (VR) is one such product, often considered the end of the line in terms of oil refining, and yet, it serves as a crucial starting point for several other industrial applications. This article delves into the world of VR, exploring its applications, chemical composition, production process, and the industries that rely on this heavy, high-boiling residue.
**Applications of Vacuum Residue (VR)**
Vacuum residue, though seemingly unwieldy and undesirable, is far from a waste product in the world of petrochemicals. It finds use in several key applications:
- **Bitumen Production**: Bitumen, a highly viscous and durable material used in road construction, roofing, and waterproofing, is often produced from vacuum residue. The high viscosity and heat resistance of VR make it an ideal starting point for the production of bitumen.
**Bitumen Production from Vacuum Residue**
Bitumen, often referred to as asphalt in North America, is a highly viscous and sticky semi-solid or liquid form of petroleum. It is primarily used in the construction and maintenance of roads, highways, airport runways, roofing, and waterproofing. Bitumen’s durability and ability to withstand high traffic loads, weather conditions, and the test of time make it a crucial material in various construction applications.
**1. Blending and Modification:**
The production of bitumen starts with the selection of an appropriate feedstock, and this is where vacuum residue comes into play. VR is an ideal starting point due to its high viscosity and heat resistance. However, to meet the specific requirements of different applications, bitumen often undergoes blending and modification processes. These processes can involve blending VR with other lighter fractions of crude oil or additives to achieve the desired performance characteristics, such as viscosity, softening point, and penetration.
**2. Oxidation:**
One of the common methods for bitumen production from VR is oxidation. In this process, air is bubbled through the VR at elevated temperatures, typically around 260-320°C (500-608°F). This controlled oxidation results in the conversion of some of the hydrocarbons in VR into polar compounds, which enhances the bitumen’s adhesion properties and durability. Oxidized bitumen is often used in roofing and waterproofing applications.
**3. Air Blowing:**
Air blowing is another method used to modify VR into bitumen. In this process, air is blown through VR at high temperatures, which causes oxidation and polymerization of the hydrocarbons. This results in increased molecular weight and viscosity, making the bitumen suitable for various applications. Air-blown bitumen is commonly used in road construction.
**4. Cutback Bitumen:**
Cutback bitumen is produced by blending bitumen with a volatile solvent, typically kerosene or diesel. The purpose of this process is to reduce the viscosity of the bitumen, making it easier to handle and apply. The solvent evaporates after application, leaving the bitumen to bind the aggregate materials. Cutback bitumen is particularly useful in road maintenance and repair work.
**5. Emulsified Bitumen:**
In some applications, bitumen is emulsified to form a stable mixture with water. This emulsification process typically involves the use of emulsifying agents and mechanical mixing. Emulsified bitumen is used for various purposes, including cold asphalt mix production and dust control on gravel roads.
**6. Polymer-Modified Bitumen (PMB):**
To enhance the performance characteristics of bitumen, polymers are often added to the mixture. This results in polymer-modified bitumen (PMB) with improved elasticity, durability, and resistance to deformation. PMB is commonly used in high-stress applications, such as heavy traffic roadways and airport runways.
**7. Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA):**
Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) is one of the most common applications of bitumen. In this process, bitumen is mixed with aggregates, typically crushed stone, sand, and filler materials, at high temperatures to produce a durable asphalt mixture used in road construction. The quality of bitumen in HMA is critical for ensuring the longevity and performance of the road surface.
**Conclusion:**
Bitumen production from vacuum residue is a critical step in the construction and infrastructure development industry. The ability to tailor bitumen’s properties to specific applications, whether through blending, oxidation, or modification, allows engineers and builders to create durable, long-lasting road surfaces, roofs, and waterproofing solutions. As the demand for infrastructure and construction projects continues to grow, the role of bitumen in these applications remains as essential as ever. The use of vacuum residue as a starting point in bitumen production ensures that this valuable resource finds new life in the form of resilient and dependable materials that benefit society at large.
2. **Heavy Fuel Oil**: Vacuum residue serves as a feedstock for the production of heavy fuel oils used in industries, power generation, and marine engines. These heavy fuels are prized for their energy density and affordability.
3. **Coking**: One of the most important applications of VR is in the coking process. In delayed coking, VR is heated to high temperatures, causing it to crack and yield valuable products such as naphtha, diesel, and petroleum coke. Petroleum coke is used in various industries, including the production of anodes for the aluminum industry and as a fuel.
4. **Hydrocracking and Hydrotreating**: VR can be subjected to hydrocracking and hydrotreating processes to break down its heavy hydrocarbons into lighter, more valuable products such as gasoline, diesel, and petrochemical feedstocks.
5. **Lubricating Oil Production**: Some vacuum residue may be further processed to produce lubricating oils, which are essential in various industries and for the automotive sector.
6. **Asphalt Production**: VR can be used in the production of asphalt, which is widely used in road construction, roofing, and other applications.
**Chemical Composition of Vacuum Residue**
The chemical composition of VR is complex and varies depending on the source of the crude oil it is derived from. However, some common elements and compounds found in VR include:
– **High Molecular Weight Hydrocarbons**: VR contains heavy, long-chain hydrocarbons with high molecular weights. These are responsible for its high viscosity and low volatility.
– **Sulfur**: Sulfur is often present in VR, and its removal is essential for meeting environmental regulations and producing cleaner products.
– **Metals**: VR may contain trace amounts of metals, which can have detrimental effects on downstream processes if not removed.
– **Asphaltenes**: Asphaltenes are complex, high-molecular-weight compounds that contribute to the high viscosity of VR. They are often a challenge to handle in refining processes.
– **Resins**: Resins are intermediate between asphaltenes and lighter hydrocarbons, contributing to the overall composition of VR.
**Production Process**
The production of vacuum residue occurs within the vacuum distillation unit of an oil refinery. Here’s a simplified overview of the process:
1. **Atmospheric Distillation**: Crude oil is first heated and passed through an atmospheric distillation tower. This separates it into various fractions based on boiling points, with lighter components rising and heavier ones descending.
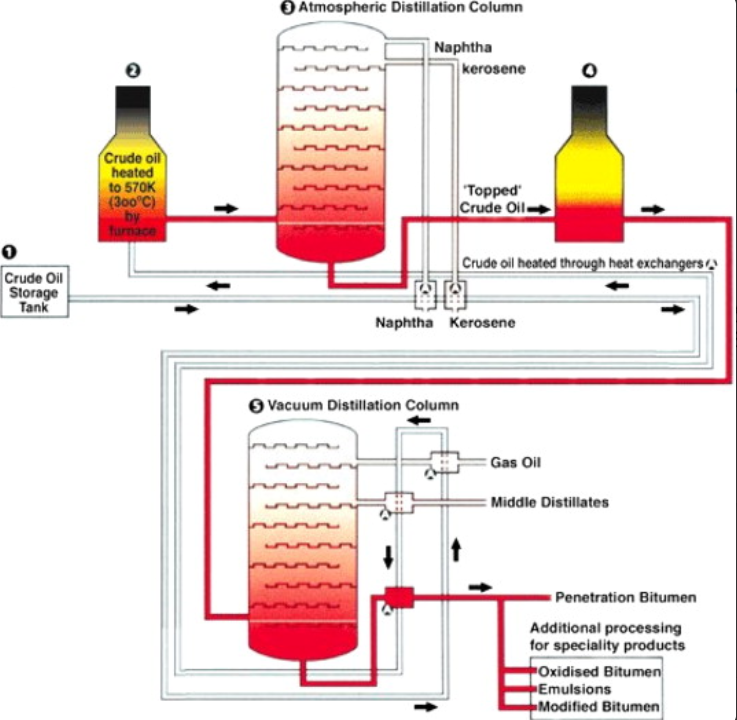
2. **Residues and Vacuum Distillation**: The heaviest fraction, often referred to as “residues,” is further processed in a vacuum distillation unit. In this unit, the pressure is lowered, and the temperature is carefully controlled to prevent cracking of the molecules. This allows the VR to be separated from the even heavier components, such as the atmospheric bottoms.
3. **Cooling and Storage**: The vacuum residue is then cooled and stored in tanks for further use or processing. It is at this stage that various industries and processes may choose to use VR as a feedstock.
**Applicable Industries**
A range of industries relies on vacuum residue for various purposes. These industries include:
1. **Construction**: Bitumen derived from VR is used in road construction, roofing, and waterproofing.
2. **Energy**: Heavy fuel oils produced from VR are used in power generation and industrial heating applications.
3. **Petrochemicals**: The petrochemical industry benefits from VR through hydrocracking and hydrotreating processes that convert it into valuable feedstocks.
4. **Transportation**: Marine engines and certain industrial applications use heavy fuel oils produced from VR.
5. **Automotive**: Lubricating oils produced from VR play a crucial role in the automotive sector.
6. **Aluminum Production**: Petroleum coke, a byproduct of coking VR, is used in the aluminum industry.
7. **Roofing and Waterproofing**: Asphalt produced from VR is used in roofing and waterproofing materials.
8. **Environmental Remediation**: Some applications involve using VR in environmental remediation, such as in the creation of barriers to contain or control pollution.
**Conclusion**
Vacuum residue, despite being the heaviest and most challenging product of crude oil refining, is a valuable resource with a wide range of applications. Its chemical composition, production process, and utilization in various industries make it a key component in the global energy and manufacturing landscape. Understanding VR and its versatility is crucial for managing resources efficiently and maximizing the benefits of crude oil refining in a sustainable manner.
As industries continue to evolve, the role of vacuum residue in providing essential materials and energy sources remains vital. Whether it’s in the construction of roads, the production of energy, or the creation of petrochemical feedstocks, VR plays a fundamental role in meeting the needs of a growing and dynamic world.
Vista Asman Company is a supplier of all kinds of oil derivatives and oil products (base oils) in different grades from the best sources at the best price with the ability to export to all safe ports in the world. Contact us for more information